(ainda não pus a legenda das imagens )
Requisitos :
- Netbeans 7.2
- spring-3.2.0.M2 -- link direto
- estar com o banco mysql springlessons, e a tabela contato criada. ver lição 4,5, 6 ou 7
- Struts 1.3.10 (utilizarei a dist que já vem com o NB)
- Ter lido :
Posts Anteriores :
JSNBTut - Lesson 01 - introdução ao Spring
JSNBTut - Lesson 02 - introdução ao gerenciamento de dependências no SpringJSNBTut - Lesson 03 - acessando banco de dados Mysql com beans e injeção de dependências
JSNBTut - Lesson 04 - outro jeito rápido de utilizar o Spring e Mysql sem utilizar Arquivos XML.
JSNBTut - Lesson 05 - comparação entre as implementações e introdução ao Swing. Jtable + DefaultTableModel e implementação de uma TableModel, ...
Obrigatório:
JSNBTut - Lesson 06 - implementando um CRUD ao exemplo , que é o projeto que continuaremos neste post.
- Finalizando o CRUD completo em Java utilizando Swing e Spring
- Implementamos um validador com org.springframework.validation.Validator
- Implementamos um Tema
- Vimos como importar /exportar arquivos XML usando XStream
- Aprendemos a usar Anotações
- Implementamos um SplashScreen
- Aprendemos a distribuir nossa aplicação e customizar o build do projeto no build.xml
Lembrando a estrutura da nossa tabela do mysql
 |
| Figura 01 - Tabela Contato |
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `springlessons`.`contato` ( `id` INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT , `nome` VARCHAR(45) NULL , `telefone` VARCHAR(45) NULL , PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE = InnoDB
OBS : as vezes o nome do meu servidor Mysql pode aparece como ns1 (quando estou no escritório) ou localhost (quando estou no lap). Relax, o banco é o mesmo, ok ?
Este é o 8º da série , o objetivo deste post é implementar o programa que terminamos na lição 07 na web. Para isso utilizaremos o framework Struts, e depois integraremos com o Spring.
Algumas info antes de criar o projeto web. Quando se trata de JSP, já existem alguns padrões de implementação e organização dos arquivos :
1) Vendo a organização do projeto (arquivos e pastas)
I ) exemplo criado com o o Maven :Comando : mvn archetype:generate -DgroupId=com.myapp -DartifactId=meuscontatos-webapp -DarchetypeArtifactId=maven-archetype-webapp
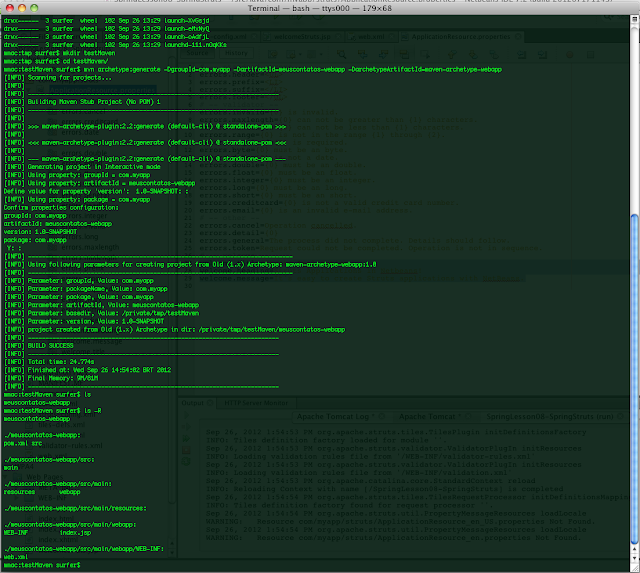 |
| Figura 02 - Gerando um projeto baseado no Maven |
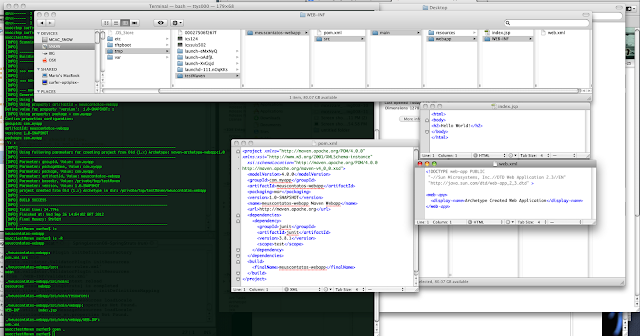 |
| Figura 03 - Arquivos gerado pelo mvn |
II) o Struts fornece um exemplo também p/ iniciar um projeto, após descompactar a lib do struts veja a pasta apps tem um arquivo struts-blank-1.3.10.war (que é um zip. descompacte esse arquivo)
 |
| Figura 04 - Exemplos do struts 1 |
 |
| Figura 05 - Arquivos do exemplo |
Então vimos que uma webApp contém a seguinte estrutura (com variações de implementação):
Projeto
--src
--conf : arquivo Manifest
--java : packages e classes Java e arquivos .properties
--web ouWebContent
---META-INF
--context.xml
---WEB-INF
--Arquivos.xml ; normalmente aqui vão o web.xml. o beans.xml, struts-config.xml e TLDs
--Arquivos JSP e html, images, js, css, etc..
então vamos criar a webapp no NB:
2) Criando o Projeto Web
 |
| Figura 06 - Novo Projeto |
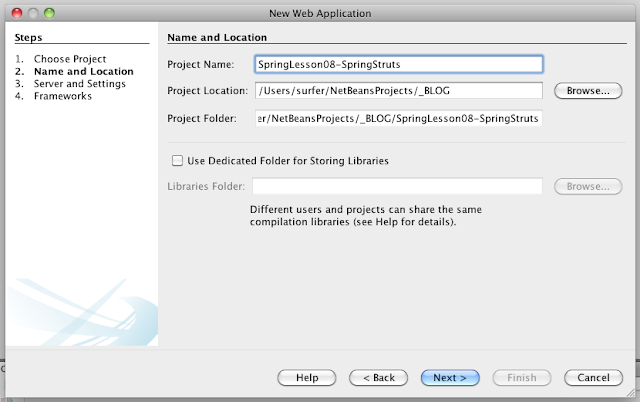 |
| Figura 07 - Nome do projeto |
 |
| Figura 08 - Defina Servidor Tomcat ou GlassFish |
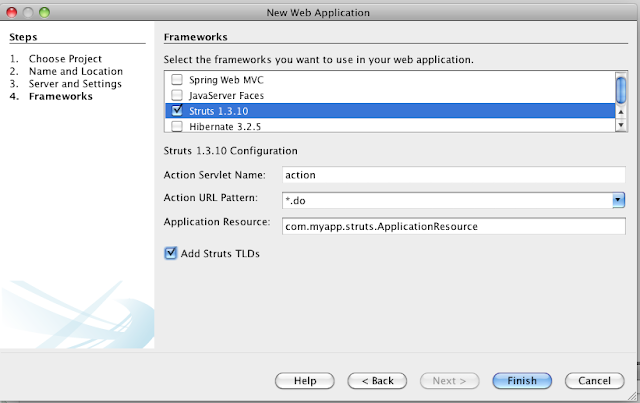 |
| Figura 09 - Adicionando o Struts 1.3.10 que vem com o NB |
 |
| Figura 10 - Projeto com a inclusão do Struts |
 |
| Figura 11 - Teste o projeto |
 |
| Figura 12 - Teste pelo Run Projet |
 |
| Figura 13 - Teste pelo Run Projet pasando a URL na mão |
 |
| Figura 14 - Output do NB |
Nossa aplicação contém arquivos XML que definem o comportamento dos servlets e algumas configurações.
I) Ao carregar a app,
O arquivo struts-config.xml informou uma action de nome Welcome apontado /Welcome.do
Veja o nosso arquivo struts-config.xml sem os comentários :
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE struts-config PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 1.3//EN"
"http://jakarta.apache.org/struts/dtds/struts-config_1_3.dtd">
<struts-config>
<form-beans>
</form-beans>
<global-exceptions>
</global-exceptions>
<global-forwards>
<forward name="welcome" path="/Welcome.do"/>
</global-forwards>
<action-mappings>
<action path="/Welcome" forward="/welcomeStruts.jsp"/>
</action-mappings>
<controller processorClass="org.apache.struts.tiles.TilesRequestProcessor"/>
<message-resources parameter="com/myapp/struts/ApplicationResource"/>
<!-- ========================= Tiles plugin ===============================-->
<!-- ..... Paths found in Tiles definitions are relative to the main context.
-->
<plug-in className="org.apache.struts.tiles.TilesPlugin" >
<set-property property="definitions-config" value="/WEB-INF/tiles-defs.xml" />
<set-property property="moduleAware" value="true" />
</plug-in>
<!-- ========================= Validator plugin ================================= -->
<plug-in className="org.apache.struts.validator.ValidatorPlugIn">
<set-property
property="pathnames"
value="/WEB-INF/validator-rules.xml,/WEB-INF/validation.xml"/>
</plug-in>
</struts-config>
II) e de onde vem esse .do no fim da solicitação http ?
R: da configuração do arquivo web.xml, observe a inicial :
Atenção :
- Na linha <load-on-startup>2</load-on-startup> dentro da tag <servlet>
- No conjunto <jsp-config> que adicionei as TLDs junto com o projeto. Pode-se usar a url do site, mas e se a WebApp estiver num servidor que não acessa a Internet ?
- E o .do está sendo "resolvido" pela tag <servlet-mapping> com um pattern .do .
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app version="3.0" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd">
<servlet>
<servlet-name>action</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.apache.struts.action.ActionServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>config</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/struts-config.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>debug</param-name>
<param-value>2</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>detail</param-name>
<param-value>2</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>2</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>action</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.do</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<session-config>
<session-timeout>
30
</session-timeout>
</session-config>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
<jsp-config>
<taglib>
<taglib-uri>/WEB-INF/struts-bean.tld</taglib-uri>
<taglib-location>/WEB-INF/struts-bean.tld</taglib-location>
</taglib>
<taglib>
<taglib-uri>/WEB-INF/struts-html.tld</taglib-uri>
<taglib-location>/WEB-INF/struts-html.tld</taglib-location>
</taglib>
<taglib>
<taglib-uri>/WEB-INF/struts-logic.tld</taglib-uri>
<taglib-location>/WEB-INF/struts-logic.tld</taglib-location>
</taglib>
<taglib>
<taglib-uri>/WEB-INF/struts-nested.tld</taglib-uri>
<taglib-location>/WEB-INF/struts-nested.tld</taglib-location>
</taglib>
<taglib>
<taglib-uri>/WEB-INF/struts-tiles.tld</taglib-uri>
<taglib-location>/WEB-INF/struts-tiles.tld</taglib-location>
</taglib>
</jsp-config>
</web-app>
III) é chamado o arquivo welcomeStruts.jsp :
 |
| Figura 15 - arquivo welcomeStruts.jsp |
Observe as linhas : <beans:message> a chave (key) welcome.Propriedade
IV) Essa definições estão no arquivo ApplicationResource.properties dentro do package com.app.struts
 |
| Figura 16 - Arquivo properties |
observe as linhas finais :
welcome.title=Struts Application
welcome.heading=Struts Applications in Netbeans!
welcome.message=It's easy to create Struts applications with NetBeans.
3) Implementando nossas classes ao projeto:
Vamos manipular a tabela contato do banco, certo ? Precisamos de :
0) adicionar o driver do Mysql ao projeto
1) um modelo Contato
2) uma interface DAO
3) uma classe que implemente a interface DAO
4) uma interface de Serviço
5) uma classe que implemente a interface de Serviço
6) das classes p/ atender os actions que serão mapeados no arquivo struts-config.xml, que extendem a classe org.apache.struts.action.Action,
7) definir as actions e mappings no arquivo struts-config.xml
8) criar a view (interface para o usuário), definindo um form
9) criar uma página que mostre os erros quando acontecer
9) criar uma página que mostre os erros quando acontecer
OBS: ainda não vou utilizar o spring, depois implementaremos:
Mãos a obra..
defina 3 variávess:
int id;
String nome;
String telefone , e escolha refactor>> encapsulate Fields
CODE
CODE
CODE
CODE
CODE
dentro de um novo package ...action
- CreateContatoAction.java
- ContatoForm.java
- RedirectContatoAction.java
I) CreateContatoAction.java
CODE
II) ContatoForm.java
CODE
III) RedirectContatoAction.java
CODE
0) Adicione a Lib do Mysql:
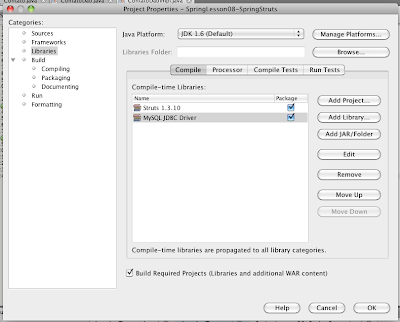 |
| Figura 17 - Adicione a lib do Mysql |
1) Criando o modelo :
 |
| Figura 18 - Criando o modelo Contato |
defina 3 variávess:
int id;
String nome;
String telefone , e escolha refactor>> encapsulate Fields
 |
| Figura 19 - Encapsulando a classe Contato |
CODE
package com.myapp.model;
public class Contato {
private int id;
private String nome;
private String telefone;
public Contato() {
this.id=0;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getNome() {
return nome;
}
public void setNome(String nome) {
this.nome = nome;
}
public String getTelefone() {
return telefone;
}
public void setTelefone(String telefone) {
this.telefone = telefone;
}
}
2) Criando uma interface DAO
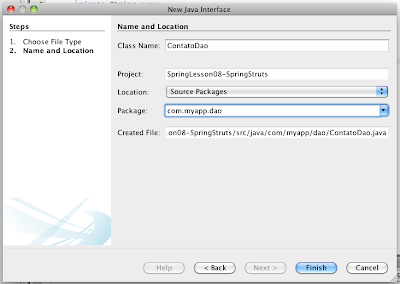 |
| Figura 20 - Interface DAO |
CODE
package com.myapp.dao;
import com.myapp.model.Contato;
import java.util.List;
public interface ContatoDao {
public void create(Contato contato);
public List<Contato> findAll();
}
3) Criando uma classe que implemente a interface DAO
 |
| Figura 21- Criando a implementação da interface |
 |
| Figura 22 - nome da Classe de implementação |
CODE
package com.myapp.dao;
import com.myapp.model.Contato;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.logging.Level;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
public class ContatoDaoImpl implements ContatoDao {
static {
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
} catch (Exception ex) {
Logger.getLogger(ContatoDaoImpl.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex);
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(ex);
}
}
private Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://ns1/springlessons", "springlessons", "DHADdSXcDF29WGXy");
}
@Override
public void create(Contato contato) {
Connection Con = null;
PreparedStatement pstm = null;
try {
Con = getConnection();
String sql = "INSERT INTO `springlessons`.`contato`"
+ "(`nome`,`telefone`)"
+ " VALUES (?,?)";
pstm = Con.prepareStatement(sql);
pstm.setString(1, contato.getNome());
pstm.setString(2, contato.getTelefone());
pstm.executeUpdate();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
try {
pstm.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
Logger.getLogger(ContatoDaoImpl.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, e);
}
try {
Con.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
Logger.getLogger(ContatoDaoImpl.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, e);
}
}
}
@Override
public List<Contato> findAll() {
Connection Con = null;
PreparedStatement pstm = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
Con = getConnection();
String sql = "SELECT `contato`.`id`,`contato`.`nome`,`contato`.`telefone`"
+ " FROM `springlessons`.`contato`";
pstm = Con.prepareStatement(sql);
List<Contato> contatos = new ArrayList<Contato>();
rs = pstm.executeQuery(sql);
while (rs.next()) {
Contato contato = new Contato();
contato.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
contato.setNome(rs.getString("nome"));
contato.setTelefone(rs.getString("telefone"));
contatos.add(contato);
}
return contatos;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
try {
pstm.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
Logger.getLogger(ContatoDaoImpl.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, e);
}
try {
Con.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
Logger.getLogger(ContatoDaoImpl.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, e);
}
}
}
}
4) Criando uma interface de Serviço
 |
| Figura 23 - criando a interface de Serviço |
CODE
package com.myapp.service;
import com.myapp.model.Contato;
import java.util.List;
public interface ContatoService {
public void create(Contato contato);
public List<Contato> findAll();
}
5) Criando uma classe que implemente a interface de Serviço
 |
| Figura 24 - Implemente a interface |
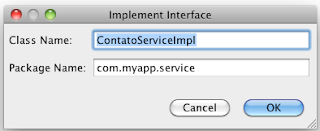 |
| Figura 25 - nome da implementação |
CODE
package com.myapp.service;
import com.myapp.dao.ContatoDao;
import com.myapp.dao.ContatoDaoImpl;
import com.myapp.model.Contato;
import java.util.List;
public class ContatoServiceImpl implements ContatoService {
private ContatoDao dao = new ContatoDaoImpl();
@Override
public void create(Contato contato) {
dao.create(contato);
}
@Override
public List<Contato> findAll() {
return dao.findAll();
}
}
6) Criando as classes p/ atender os actions que serão mapeados no arquivo struts-config.xml, que extendem a classe org.apache.struts.action.Action,
dentro de um novo package ...action
- CreateContatoAction.java
- ContatoForm.java
- RedirectContatoAction.java
I) CreateContatoAction.java
 |
| Figura 26 - Criando a Action |
CODE
package com.myapp.action;
import com.myapp.model.Contato;
import com.myapp.service.ContatoService;
import com.myapp.service.ContatoServiceImpl;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanUtils;
import org.apache.struts.action.Action;
import org.apache.struts.action.ActionForm;
import org.apache.struts.action.ActionForward;
import org.apache.struts.action.ActionMapping;
public class CreateContatoAction extends Action {
private ContatoService userService = new ContatoServiceImpl();
public void setContatoService(ContatoService userService) {
this.userService = userService;
}
@Override
public ActionForward execute(
ActionMapping mapping,
ActionForm form,
HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// return super.execute(mapping, form, request, response);
ContatoForm contatoForm = (ContatoForm) form;
Contato contato = new Contato();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(contato, contatoForm);
userService.create(contato);
return mapping.findForward("list");
}
}
II) ContatoForm.java
 |
| Figura 27 - mande o NB criar essa classe no package action |
CODE
package com.myapp.action;
import org.apache.struts.action.ActionForm;
public class ContatoForm extends ActionForm {
private String nome;
private String telefone;
public ContatoForm() {
}
public String getNome() {
return nome;
}
public void setNome(String nome) {
this.nome = nome;
}
public String getTelefone() {
return telefone;
}
public void setTelefone(String telefone) {
this.telefone = telefone;
}
}
III) RedirectContatoAction.java
 |
| Figura 28 - Adicionando a action de redirect |
CODE
package com.myapp.action;
import com.myapp.service.ContatoService;
import com.myapp.service.ContatoServiceImpl;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.apache.struts.action.Action;
import org.apache.struts.action.ActionForm;
import org.apache.struts.action.ActionForward;
import org.apache.struts.action.ActionMapping;
public class RedirectContatoAction extends Action {
private ContatoService contatoService = new ContatoServiceImpl();
public void setContatoService(ContatoService contatoService) {
this.contatoService = contatoService;
}
@Override
public ActionForward execute(
ActionMapping mapping,
ActionForm form,
HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// return super.execute(mapping, form, request, response);
request.setAttribute("contatos", contatoService.findAll());
return mapping.findForward("sucess");
}
}
7) Definindo as actions e mappings no arquivo struts-config.xml
Xml<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE struts-config PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 1.3//EN"
"http://jakarta.apache.org/struts/dtds/struts-config_1_3.dtd">
<struts-config>
<form-beans>
<form-bean name="contatoForm"
type="com.myapp.action.ContatoForm">
</form-bean>
</form-beans>
<global-exceptions>
<exception
type="java.lang.Exception"
key="user.global.ex"
path="/error.jsp" />
</global-exceptions>
<global-forwards>
<forward name="welcome" path="/Welcome.do"/>
</global-forwards>
<action-mappings>
<action path="/Welcome" forward="/welcomeStruts.jsp"/>
<action
path="/RedirectContato"
type="com.myapp.action.RedirectContatoAction">
<forward
name="sucess"
path="/index.jsp">
</forward>
</action>
<action
path="/CreateContato"
type="com.myapp.action.CreateContatoAction"
name="contatoForm"
input="/RedirectContato.do">
<forward
name="list"
path="/RedirectContato.do">
</forward>
</action>
<!-- samples
<action
path="/"
type="com.myapp."
name=""
scope=""
validate=""
input="" />
</action-mappings>
-->
</action-mappings>
<controller processorClass="org.apache.struts.tiles.TilesRequestProcessor"/>
<message-resources parameter="com/myapp/struts/ApplicationResource"/>
<plug-in className="org.apache.struts.tiles.TilesPlugin" >
<set-property property="definitions-config" value="/WEB-INF/tiles-defs.xml" />
<set-property property="moduleAware" value="true" />
</plug-in>
<!-- ========================= Validator plugin ================================= -->
<plug-in className="org.apache.struts.validator.ValidatorPlugIn">
<set-property
property="pathnames"
value="/WEB-INF/validator-rules.xml,/WEB-INF/validation.xml"/>
</plug-in>
</struts-config>
9) criar uma página que mostre os erros quando acontecer
 |
| Figura 30 - Preparando uma página p/ mostrar os erros |
 |
| Figura 31 - Página error.jsp |
o projeto deve estar assim :
 |
| Figura 32 - Estrutura do projeto até esse ponto |
3) Testando o Projeto Web
Run>> Project
 |
| Figura 33 - Testando a app |
 |
| Figura 34 - Testando a app, mais um cadastro |
 |
| Figura 35 - O programa em Swing da lição anterior acessando a mesma tabela que a pagina |
Mas está com um comportamento estranho:
1º mostra uma tela de cadastro e ao cadastrar mostra a lista dos cadastrados.Porquê ?
Se quisermos entrar direto na lista completa precisamos acessar pelo seguinte endereço na url :
http://localhost:8080/SpringLesson08-SpringStruts/RedirectContato.do
e o link p/ acessa a pagina criada pelo NB+Struts hello, por esse http://localhost:8080/SpringLesson08-SpringStruts/Welcome.do
Como acertamos isso ? Bom tem centenas de jeitos, vamos fazer o mais simples 1º
I) defina como index.html no arquivo web.xml
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
e no index.html aponte p/ o mapping desejado :
<html>
<head>
<title></title>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
location.href='/SpringLesson08-SpringStruts/RedirectContato.do';
</script>
</body>
</html>
II) Salve os arquivos, o NB automaticamente faz o Deploy da app,clique em Run. veja se o apontamento do arquivo html funcionou.
Vou fornecer a versão 1 do projeto como está até aqui.
SpringLesson08-SpringStruts-v1
4) Implementando o Spring ao projeto com o struts.
1) adicione a lib do spring ao projeto
 |
| Figura 36 - Adicionando a lib do Spring |
2) altere o struts-config.xml
Xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE struts-config PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 1.3//EN"
"http://jakarta.apache.org/struts/dtds/struts-config_1_3.dtd">
<struts-config>
<form-beans>
<form-bean name="contatoForm"
type="com.myapp.action.ContatoForm">
</form-bean>
</form-beans>
<global-exceptions>
<exception
type="java.lang.Exception"
key="user.global.ex"
path="/error.jsp" />
</global-exceptions>
<global-forwards>
<forward name="welcome" path="/Welcome.do"/>
</global-forwards>
<action-mappings>
<action path="/Welcome" forward="/welcomeStruts.jsp"/>
<action
path="/RedirectContato">
<forward
name="sucess"
path="/index.jsp">
</forward>
</action>
<action
path="/CreateContato"
name="contatoForm"
input="/RedirectContato.do">
<forward
name="list"
path="/RedirectContato.do">
</forward>
</action>
<!-- renomeado apos adicionar o spring
<action
path="/CreateContato"
type="com.myapp.action.CreateContatoAction"
name="contatoForm"
input="/RedirectContato.do">
<forward
name="list"
path="/RedirectContato.do">
</forward>
</action>
<action
path="/RedirectContato"
type="com.myapp.action.RedirectContatoAction">
<forward
name="sucess"
path="/index.jsp">
</forward>
</action>
-->
<!-- samples
<action
path="/"
type="com.myapp."
name=""
scope=""
validate=""
input="" />
</action-mappings>
-->
</action-mappings>
<controller>
<set-property
property="processorClass"
value="org.springframework.web.struts.DelegatingRequestProcessor" />
</controller>
<message-resources parameter="MessageResources"/>
<plug-in className="org.springframework.web.struts.ContextLoaderPlugIn" >
</plug-in>
<!-- <controller processorClass="org.apache.struts.tiles.TilesRequestProcessor"/>
<message-resources parameter="com/myapp/struts/ApplicationResource"/>
<plug-in className="org.apache.struts.tiles.TilesPlugin" >
<set-property property="definitions-config" value="/WEB-INF/tiles-defs.xml" />
<set-property property="moduleAware" value="true" />
</plug-in>
========================= Validator plugin =================================
<plug-in className="org.apache.struts.validator.ValidatorPlugIn">
<set-property
property="pathnames"
value="/WEB-INF/validator-rules.xml,/WEB-INF/validation.xml"/>
</plug-in>-->
</struts-config>
3) crie o arquivo action-servlet.xml
Xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE beans PUBLIC
"-//SPRING//DTD BEAN 2.0//EN" "http://www.springframework.org/dtd/spring-beans-2.0.dtd">
<beans>
<bean name="/CreateContato"
class="com.myapp.action.CreateContatoAction">
<property name="contatoService"></property>
</bean>
<bean name="/RedirectContato"
class="com.myapp.action.RedirectContatoAction">
<property name="contatoService"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="contatoService"
class="com.myapp.service.ContatoServiceImpl">
<!--<property name="contatoDao"> isso causa um erro o correto esta abaixo-->
<property name="dao">
<!-- injeção da dependência-->
<bean
id="contatoDao"
class="com.myapp.dao.ContatoDaoImpl">
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
4) salve os arquivos modificados.
5) teste o programa e veja o Log do NB:
Não deve conter nenhum erro, se tiver verifique as configurações nos arquivos XML
Sep 27, 2012 1:02:18 PM org.springframework.web.struts.ContextLoaderPlugIn init INFO: ContextLoaderPlugIn for Struts ActionServlet 'action, module '': initialization started Sep 27, 2012 1:02:18 PM org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext prepareRefresh INFO: Refreshing WebApplicationContext for namespace 'action-servlet': startup date [Thu Sep 27 13:02:18 BRT 2012]; root of context hierarchy Sep 27, 2012 1:02:19 PM org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader loadBeanDefinitions INFO: Loading XML bean definitions from ServletContext resource [/WEB-INF/action-servlet.xml] Sep 27, 2012 1:02:20 PM org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory preInstantiateSingletons INFO: Pre-instantiating singletons in org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory@fe2254a: defining beans [/CreateContato,/RedirectContato]; root of factory hierarchy Sep 27, 2012 1:02:21 PM org.springframework.web.struts.ContextLoaderPlugIn initWebApplicationContext INFO: Using context class 'org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext' for servlet 'action' Sep 27, 2012 1:02:21 PM org.springframework.web.struts.ContextLoaderPlugIn init INFO: ContextLoaderPlugIn for Struts ActionServlet 'action', module '': initialization completed in 2610 ms Sep 27, 2012 1:02:21 PM org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase start INFO: The start() method was called on component [StandardEngine[Catalina].StandardHost[localhost].StandardContext[/SpringLesson08-SpringStruts]] after start() had already been called. The second call will be ignored.
6) altere as actions no package actions
CODE
package com.myapp.action;
import com.myapp.model.Contato;
import com.myapp.service.ContatoService;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanUtils;
import org.apache.struts.action.Action;
import org.apache.struts.action.ActionForm;
import org.apache.struts.action.ActionForward;
import org.apache.struts.action.ActionMapping;
public class CreateContatoAction extends Action {
// private ContatoService userService = new ContatoServiceImpl();
// com o Spring
private ContatoService contatoService;
public void setContatoService(ContatoService userService) {
this.contatoService = userService;
}
@Override
public ActionForward execute(
ActionMapping mapping,
ActionForm form,
HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// return super.execute(mapping, form, request, response);
ContatoForm contatoForm = (ContatoForm) form;
Contato contato = new Contato();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(contato, contatoForm);
contatoService.create(contato);
return mapping.findForward("list");
}
}
CODE
package com.myapp.action;
import com.myapp.service.ContatoService;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.apache.struts.action.Action;
import org.apache.struts.action.ActionForm;
import org.apache.struts.action.ActionForward;
import org.apache.struts.action.ActionMapping;
public class RedirectContatoAction extends Action {
// private ContatoService contatoService = new ContatoServiceImpl();
// com o Spring
private ContatoService contatoService ;
public void setContatoService(ContatoService contatoService) {
this.contatoService = contatoService;
}
@Override
public ActionForward execute(
ActionMapping mapping,
ActionForm form,
HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// return super.execute(mapping, form, request, response);
request.setAttribute("contatos", contatoService.findAll());
return mapping.findForward("sucess");
}
}
7) altere a classe dao.ContatoServiceImpl
CODE
package com.myapp.service;
import com.myapp.dao.ContatoDao;
import com.myapp.model.Contato;
import java.util.List;
public class ContatoServiceImpl implements ContatoService {
// private ContatoDao dao = new ContatoDaoImpl();
// depois do spring
private ContatoDao dao;
@Override
public void create(Contato contato) {
getDao().create(contato);
}
@Override
public List<Contato> findAll() {
return getDao().findAll();
}
}
8) compile e teste. veja o erro :
Log
Offending resource: ServletContext resource [/WEB-INF/action-servlet.xml] Bean '/CreateContato'; nested exception is org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.BeanDefinitionParsingException: Configuration problem: <property> element for property 'contatoService' must specify a ref or value Offending resource: ServletContext resource [/WEB-INF/action-servlet.xml] Bean '/CreateContato' -> Property 'contatoService' at org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.FailFastProblemReporter.error(FailFastProblemReporter.java:68) at org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.ReaderContext.error(ReaderContext.java:85)
9) acerte o arquivo action-servlet.xml e adicione as ref
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE beans PUBLIC
"-//SPRING//DTD BEAN 2.0//EN" "http://www.springframework.org/dtd/spring-beans-2.0.dtd">
<beans>
<bean name="/CreateContato"
class="com.myapp.action.CreateContatoAction">
<property name="contatoService" ref="contatoService"></property>
</bean>
<bean name="/RedirectContato"
class="com.myapp.action.RedirectContatoAction">
<property name="contatoService" ref="contatoService"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="contatoService"
class="com.myapp.service.ContatoServiceImpl">
<!--<property name="contatoDao"> isso causa um erro o correto esta abaixo-->
<property name="dao">
<!-- injeção da dependência-->
<bean
id="contatoDao"
class="com.myapp.dao.ContatoDaoImpl">
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
10) compile e teste. veja o erro : Log
org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationException: Error creating bean with name '/CreateContato' defined in ServletContext resource [/WEB-INF/action-servlet.xml]: Cannot resolve reference to bean 'contatoService' while setting bean property 'contatoService'; nested exception is org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationException: Error creating bean with name 'contatoService' defined in ServletContext resource [/WEB-INF/action-servlet.xml]: Error setting property values; nested exception is org.springframework.beans.NotWritablePropertyException: Invalid property 'dao' of bean class [com.myapp.service.ContatoServiceImpl]: Bean property 'dao' is not writable or has an invalid setter method. Does the parameter type of the setter match the return type of the getter? at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionValueResolver.resolveReference(BeanDefinitionValueResolver.java:329)
A classe precisa dos Gets/Sets
11) encapsule a classe ContatoServiceImpl
 |
| Figura 37 - Encapsule a classe ContatoServiceImpl |
CODE
package com.myapp.service;
import com.myapp.dao.ContatoDao;
import com.myapp.model.Contato;
import java.util.List;
public class ContatoServiceImpl implements ContatoService {
// private ContatoDao dao = new ContatoDaoImpl();
// depois do spring
private ContatoDao dao;
@Override
public void create(Contato contato) {
getDao().create(contato);
}
@Override
public List<Contato> findAll() {
return getDao().findAll();
}
public ContatoDao getDao() {
return dao;
}
public void setDao(ContatoDao dao) {
this.dao = dao;
}
}
compile e teste.
Log
Sep 27, 2012 1:43:55 PM org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext prepareRefresh INFO: Refreshing WebApplicationContext for namespace 'action-servlet': startup date [Thu Sep 27 13:43:55 BRT 2012]; root of context hierarchy Sep 27, 2012 1:43:55 PM org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader loadBeanDefinitions INFO: Loading XML bean definitions from ServletContext resource [/WEB-INF/action-servlet.xml] Sep 27, 2012 1:43:55 PM org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory preInstantiateSingletons INFO: Pre-instantiating singletons in org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory@3e898802: defining beans [/CreateContato,/RedirectContato,contatoService]; root of factory hierarchy Sep 27, 2012 1:43:56 PM org.springframework.web.struts.ContextLoaderPlugIn initWebApplicationContext INFO: Using context class 'org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext' for servlet 'action' Sep 27, 2012 1:43:56 PM org.springframework.web.struts.ContextLoaderPlugIn init INFO: ContextLoaderPlugIn for Struts ActionServlet 'action', module '': initialization completed in 921 ms Sep 27, 2012 1:43:56 PM org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContext reload INFO: Reloading Context with name [/SpringLesson08-SpringStruts] is completed
12) Teste. experimente fazer mais um cadastro.
 |
| Figura 38 - Testando a app de novo |
13) se tivéssemos outros objetos e tabelas precisaríamos da conexão compartilhada entre os DAOs.
 |
| Figura 39 - Crie a classe de conexão ao Mysql |
CODE
package com.myapp.dao;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.logging.Level;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
public class ConexaoMysql {
private Connection Conexao;
public ConexaoMysql() {
connect();
}
static {
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
} catch (Exception ex) {
Logger.getLogger(ConexaoMysql.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex);
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(ex);
}
}
public Connection getConexao() {
return Conexao;
}
public final void connect() {
try {
this.Conexao = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://ns1/springlessons", "springlessons", "DHADdSXcDF29WGXy");
} catch (SQLException ex) {
Logger.getLogger(ConexaoMysql.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex);
}
}
}
14) altere o contatoDaoImpl p/ usar essa conexão :
CODE
package com.myapp.dao;
import com.myapp.model.Contato;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.logging.Level;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
public class ContatoDaoImpl implements ContatoDao {
ConexaoMysql Conexao = new ConexaoMysql();
@Override
public void create(Contato contato) {
Connection Con = this.Conexao.getConexao();
PreparedStatement pstm = null;
try {
// Con = getClass();
String sql = "INSERT INTO `springlessons`.`contato`"
+ "(`nome`,`telefone`)"
+ " VALUES (?,?)";
pstm = Con.prepareStatement(sql);
pstm.setString(1, contato.getNome());
pstm.setString(2, contato.getTelefone());
pstm.executeUpdate();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
try {
pstm.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
Logger.getLogger(ContatoDaoImpl.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, e);
}
try {
Con.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
Logger.getLogger(ContatoDaoImpl.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, e);
}
}
}
@Override
public List<Contato> findAll() {
Connection Con = this.Conexao.getConexao();
PreparedStatement pstm = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
// Con = getConnection();
String sql = "SELECT `contato`.`id`,`contato`.`nome`,`contato`.`telefone`"
+ " FROM `springlessons`.`contato`";
pstm = Con.prepareStatement(sql);
List<Contato> contatos = new ArrayList<Contato>();
rs = pstm.executeQuery(sql);
while (rs.next()) {
Contato contato = new Contato();
contato.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
contato.setNome(rs.getString("nome"));
contato.setTelefone(rs.getString("telefone"));
contatos.add(contato);
}
return contatos;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
try {
pstm.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
Logger.getLogger(ContatoDaoImpl.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, e);
}
try {
Con.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
Logger.getLogger(ContatoDaoImpl.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, e);
}
}
}
}
Salve, e teste:
 |
| Figura 40 - Testando a app a pós as alterações |
E assim integramos o struts 1.3.10 com o Spring 3.2
Projeto NB
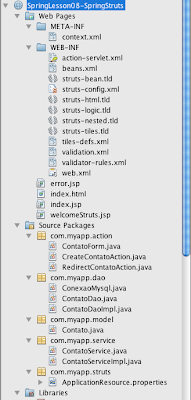 |
| Figura 41a - Arquivos do projeto |
 |
| Figura 41b - Arquivos do projeto |
Como este projeto tem propósitos educacionais , os frameworks são libs do NB, e estão incluídas inteiras com todas as deps.
Fica como lição de casa, adicionar manualmente apenas as libs utilizadas.
 |
| Figura 42 - Libs utilizadas do projeto |
Download do projeto NB
SpringLesson08-SpringStruts-v2
Resumo, o que vimos :
- Organização de projetos WEB
- Implementar o Struts 1.3.10
- Criamos uma interface contatoDAO
- Implementamos a interface com a classe ContatoDaoImpl
- Criamos uma interface de Serviço ContatoService
- Implementamos a interface com a classe ContatoServiceImpl
- Criamos as classes p/ atender os actions que são mapeados no arquivo struts-config.xml, que extendem a classe org.apache.struts.action.Action
- Definimos as actions e mappings no arquivo struts-config.xml
- Criamos uma view através de um arquivo index.jsp
- Criamos uma vier p/ mostrar os erros
- Integramos o Spring 3 com o Struts 2
- Definimos nossos beans no arquivo action-servlet.xml
- Vimos nos logs a ordem em que as classes são instanciadas e como localizar erros
- Compartilhamos a conexão através de uma classe ConexaoMysql
- Testamos o cadastro e vimos funcionando
humm e como ficaria essa implementação com o Struts 2?
até o próximo post...

Nenhum comentário:
Postar um comentário